The Evolution of Search Engine Crawlers and CMS
I have been in the industry for more than 20 years. When Googlebot first started, it could only crawl and index text. JavaScript content, and even links in dropdown menus, were a challenge. Flash files were impossible to crawl without providing a text alternative.
Does anyone still remember prerender.io? It was a solution for websites with heavy JavaScript frameworks like Angular, which is now almost obsolete.
When mobile websites were introduced around 2010, most of our clients either didn’t have a mobile-friendly website or had websites that didn’t function well on mobile devices. A few years later, Google introduced the mobile-first approach, and mobile-friendliness became a crucial part of every audit we conducted. Do you still remember duda.co, which many people used to create mobile websites? Or AMP, introduced by Google and still in use today?
With the introduction of structured data (Schema, canonical tags, HREFlang, and more), web developers and CMS platforms faced a new challenge: how to dynamically implement these scripts into websites. Our solution for this was a Schema audit, although we haven’t sold one in over a year as of 2024.
SEO audits, when I first started, were essential for any SEO engagement, and they remained so until the early 2020s.
The Arrival of an Almost Perfect CMS!
If you have a website managed/hosted by Shopify, here’s what you can achieve almost immediately or with less than an hour of effort:
- A reliable host and clean code that will produce a fast website with strong Core Web Vitals.
- Google Analytics with enhanced eCommerce tracking can be installed in just 5 minutes.
- All required schemas are either already in place or can be quickly added to the template.
- A crawlable, indexable, mobile-friendly website.
- All sitemaps are generated and updated automatically.
If your website is on Shopify, unless someone has mistakenly blocked search engines, there’s almost nothing to audit. Your SEO provider should only need to spend a few minutes checking your robots.txt file and the indexing section in Google Search Console—and that’s it.
The same applies to Wix or any other fully hosted and managed CMS.
What about self hosted CMS like WordPress or Magento?
WordPress and Magento are great CMS platforms for SEO. Like Shopify, they offer almost every SEO feature you need, either natively or easily added without coding (using a plugin). However, they have two issues that fully managed CMS do not:
- The code is fully open for developers to edit, which increases the likelihood of mistakes.
- If hosted on an unreliable server, they may run slowly.
Those CMS platforms will rarely need a full SEO audit; a quick check-up will usually be enough.
What Should Trigger an SEO Checkup?
There are a few KPIs that need to be tracked every month for every website:
- Ranking: A group of important keywords (10-50) for the website must be tracked monthly. We can call these the "must-rank" keywords.
- Overall Google organic traffic.
- Core Web Vitals (especially LCP).
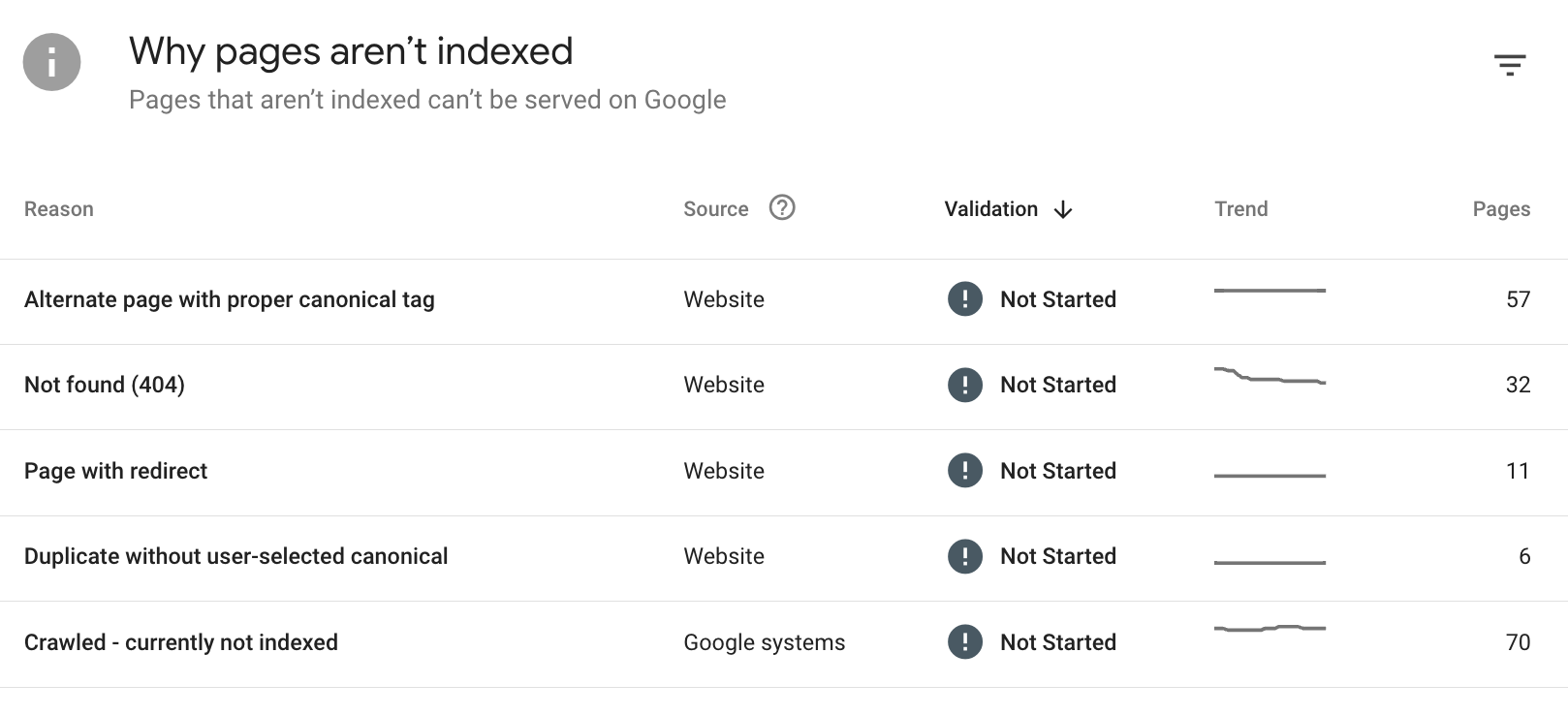
- 5XX and 4XX errors, along with other indexation data, in Google Search Console.
If there is any significant downside change of any of the KPIs above, just have a quick look at the indexation section in GSC, if you have an SEO company, they should be able to check it for you and provide an assessment quickly. Do not be intimated with the number of errors you see in GSC, I have a small website and I have a lot of them (see below):
So, what is important for SEO now, if technical SEO is less of an issue with the evolution of crawlers and CMS?
The answer hasn’t changed much in the last 20 years: it's content! You need to have the best content that your audience finds useful. To add an SEO flavour to that, here are a few content analysis and optimization actions you can take:
- Make sure your content is better than anyone else's (winning content). To assess this, Google the keyword your landing page ranks for, read the content in the first few results, and write something better. Also, optimize your title tag.
- Fill content gaps with laser-focused, winning content. If you care about a keyword, a single paragraph on a page might not be enough to rank for it—you may need a dedicated page.
- Refresh and update content for pages that are losing rankings and traffic.
- Remove, refresh, or redirect content that isn’t receiving any engagement from users or search engines.
Is Technical SEO Dead?
No, it has changed. SEO companies used to charge $10K for a technical SEO audit (without implementing any of the changes). Now, they charge much less for a quick checkup and then move on to content creation and optimization—at least the good ones do.