On-page SEO refers to any search engine optimization work you do on a website that is fully under your control (mainly on the content and the source code of the page). At this stage I assume you have completed the keyword research and the content mapping which should enable you to produce a list of URLs with one or two keywords to optimize each URL for.
Before start doing any on-page SEO you need to have some understanding to what constitutes a web page, a web page is simply a combination of HTML code, text and embedded resources (JavaScript files, CSS files and more) that are passed from a server to a browser, the browser will be able to render that combination of codes and resources into the visual web page that you see everyday, on-page optimization focuses mainly on the visible text on the page and the HTML code. In order to view the source code of a web page just do a right mouse inside the page >> click view source and you will see a code similar to the code below (just a basic page I created as an example):
This code will render in the browser like this:
It is very important to understand the visibility of each element in the HTML code to users and search engines, there are three possibilities for a web page element visibility:
- Visible to search engine crawlers only not to users but it will be used in the search engine result page SERP (e.g. description tag)
- Visible to both users and search engines (e.g. H1 tag)
- Visible mainly to search engines and social media bots with less chance to show on the SERP (e.g. structured data and rich snippet)
On-page optimization cannot be done in isolation of a marketing plan, content should appeal to users and encourage them to take certain actions, if the element is invisible to users we can possibly optimize it more for search engines.
On-page SEO in few words is making sure that key page elements like title tag, H1, URL and page content include directly or semantically the target keyword, so the keyword mention is important but it should not be done at the expense of user experience:
- If the element is visible to users on your page you have to be extremely cautious (not to damage user experience while optimizing) and focus more on users than keyword mentions (H1 tag for example)
- If the element is not visible on your page but visible in the SERP (ALT tag for example) you can be more aggressive with keyword mentions but you also need to focus on making that element more enticing to page to click
Title tag:
Visible to search engines and has a significant weight on ranking, not fully visible to users as browsers will show it in the uppers status bar and it is used in many cases by search engines as the clickable text that leads to a website in the SERP
Optimizing the title tag is a tricky process as search engines will show only 50-60 characters or no more than 300 pixels which could be 5-10 words only depending on the size of each word. The first segment of the title tag should describe what is the page about (a keyword mention is recommended in this segment) the second segment could be generic like including the brand name, example (Assuming I am optimizing a page for SEO expert):
SEO Expert 15 Years Doing SEO - Wisam Abdulaziz
You can see that the title tag includes one mention of the keyword, it has a marketing message (15 years doing SEO) then another partial mention of the target keyword (SEO), the brand name was placed at the end
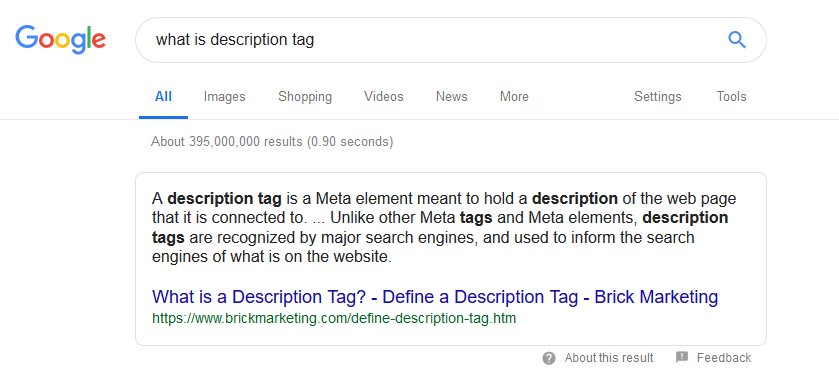
Description tag:
Visible to search engines only, doesn't have a significant weight on ranking, it is used in many cases by search engines as a snippet in the SERP which gives it a huge value from a click through rate (CTR) prospective.
Similar to title tag there is a length limit (155-160 and can go longer than that in some cases), this is a decent real-estate to deliver a good marketing message that entices people to click on your listing in the SERP, a keyword mention is still recommended as Google normally bold searched keywords inside the snippet, example:
A long career as a SEO expert where I helped more than 1000 clients to gain more exposure on search engines that lead to more traffic and business.
I have one keyword mention and a marketing message.
H1 Tag:
Every page should have a heading, some CMS (content management systems) contain it in H1, H2, or H3 others will not use any Hx tags, regardless of how your heading is coded in the page this section will speak to optimizing the first heading of a web page. H1 tags have a premium location on the page, they are always located at the top (above the fold in most cases) and totally visible to users because of that user experience and delivering the right marketing message are more important than keyword mentions as people that read H1 tags are on your website and they are potential leads or customers.
H1 tag does not have a limit on the number of characters as search engines do not use it very often in their SERP but I still do not see it going more than 10 words, example:
Check Points That an SEO Expert Can Audit for Your Website
I have a keyword mention, I tried to create some curiosity so the user will continue reading the page
Body Content:
This is what matters most to both users and search engines, the first priority here is to create a winning content that gives users the best answer to their question (search query/keyword), first thing needs to be done here is searching the target keyword on Google and visiting the top 5 or even top 10 results to find out the characteristics of a winning content for your target keyword also find out what are they missing, examples of a winning content assessment:
- Average number of words is 500 words/page
- Average number of images is 5
- There is one video on each of them
- They are missing some statistics regarding that topic
- They are missing linking out to some great resources around that topic
Now start writing your content to better the current winning content, keyword mentions normally come naturally in the body content if not one or two mentions in a user friendly manner will be suffice.
Internal Linking:
Google started their search engine based on a patent called Page Rank, which is a number from 1-10 that gives pages with a lot of links (external or internal links) more value, this concept applies also to internal linking optimization, the more internal links a page has the more authority or importance it will gain from Google which will give it a better chance to rank.
The anchor text of the internal links will pass a strong relevancy signal to search engines about the content of the destination page, so it is important to keep it as keyword rich as possible.
The easiest way to understand internal linking optimization is visiting a Wikipedia page try this one you can see every time they have content/page related to any phrase in that article they will link to it, this contextual interlinking will be passing weight or page rank to the linked pages it will also pass relevancy signals by using the keyword as an anchor text
3 ways to do internal linking:
- The Wikipedia style of internal-inking called contextual internal linking
- Optimizing the website information architecture (IA) by linking the most important pages from the upper navigation using keyword rich anchor text, while doing IA optimization it is important to keep user experience in mind as the upper navigation' main function is helping users to find content easily and quickly on the website
- Breadcrumbs navigation is a good tool that can improve user experience and help with keyword rich internal linking
Answer Box Optimization:
Goolge has 20+ types of rich snippet (refers to any result that is not the blue link with gray text beneath it), the most popular rich snippet to optimize for is the answer box which normally ranks at the top of the page (called ranking 0) ranking in this position comes normally with a very high CTR that can reach 40%, the answer box in many cases will be used in voice search results on consoles like Google Home.
Picking the right keyword to target is going to be key to achieve results here, if you do not have any chance to rank for a keyword that trigger an answer box organically on the first page (preferably top 5 spots) then find another one as your chance to take that answer box is close to zero, do not listen to those who say it is a schema play and ranking doesn't matter, in more than 90% of the cases schema has nothing to do with answer box.
Recommendations to gain answer box ranking:
- Do the regular on-page optimization you do normally for any page as explained in this section (keyword mentions in title tag, H1, body etc)
- Optimize the opening paragraph or any other paragraph in the article to answer the question (in most cases it is the keyword that triggers the answer box)
- Keep the content well structured and organized (use spaces, breaks, <ol>, <p> and other mark up tags that make a post easy to read for humans)
Recommendations to gain a list based answer box ranking (with a list inside it):
- Same recommendations above for regular answer box, make sure to include a sentence that clearly defines the purpose of the list right before the first item
- Optimize the title tag and H1 to include keywords that normally trigger the answer box with a list (Example: most popular, things to do, best, types of, steps, facts).
- Each item on the list should be distinguish it from the rest of the text, (i.e. <h2>, <strong>, <li>)
URL Optimization:
The URL of a web page is not fully visible to users (browsers use it in their upper status bar where many users do not pay attention), search engines read it and use it sometimes in the SERP but it barely has any weight on ranking (it used to have a lot of weight back in the days). You can focus more on search engines while optimizing URLs, example:
www.wisamabdulaziz.com/seo-expert
Notes:
- Do not change the URLs for existing pages only for the sake of making the URL more descriptive or keyword rich (too many things can go wrong in a process like that)
- URLs are used by search engines as content identifier, all links will be counted to a URL, changing one letter in the URL without proper 301 redirect can cause page authority loss and potentially ranking loss
- Keep the URLs clean and make sure the URL is changing when people navigate to a new page, avoid using # tags or complex special characters and keep them readable for humans
Images Optimization:
The two image elements that could be optimized for an image are both invisible, ALT tag (invisible 99% of the time) and file name. Those elements must describe the image content in few words, if you can make them keyword rich that will be good if not just focus on keeping them descriptive to the image content
Finally you need to know that the on-page optimization process applies to many other platforms like:
- Google My Business
- Youtube
- App stores like Itunes and Google play
They have very similar elements to a web page like title and description, the concept of including keywords in them and making them enticing for people to click is the same. Few other elements that are not available in a web page but available in those platforms:
- Category
- Tags
- Thumbnail


No Comments