Organic traffic 3 user journeys
When optimizing organic traffic we need to look at three different user journeys and optimize for them separately or at least keep each of them in mind while optimizing for the other one. The three user journeys to optimize organic traffic for are:
- From the search engine box where a keyword is typed and the listing is clicked in the SERP
- From the SERP to the landing page
- Checkout journey (mainly for shopping carts) or the conversion funnel for lead generation
| SERP | Landing page | Conversion funnel | |
| Measured by | CTR in GSC | Bounce rate | Conversion rate |
| Possible improvements | Better descriptions tags and title tags | Better content relevant to the query | Funnel analysis and optimization |
| Better ranking | Better layout | Forms optimization | |
| Featured snippet optimization | Professional design | ||
| Brand recognition/marketing | Better CTAs | Better CTAs | |
| Better information architecture | |||
| Better usability especially website speed | Better usability especially website speed |
I will be using Google Store demo account for most examples, I will be explaining each step using the order in the table but what you start optimizing your website do it backwards:
- Test and optimize the conversion funnel
- Test and optimize the landing page
- SERP optimization
The priority goes to utilize existing traffic and fix any major issues with the conversion funnel before trying to bring more visitors to the website.
SERP journey optimization:
Optimizing for SERP starts by checking Google Search Console performance dashboard and finding keywords with high impressions and low CTR:
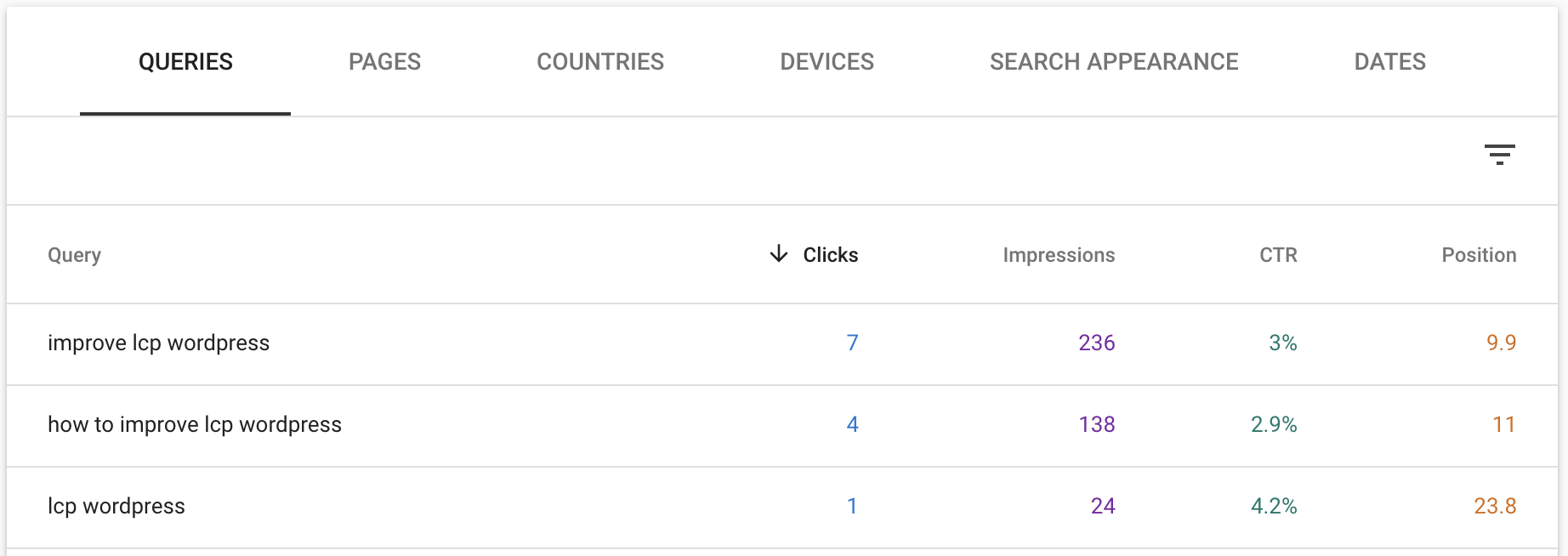
The next step will be looking up those keywords on Google to check the ranking and the snippets that Google is serving in the SERP (for my example I am checking the keyword: improve LCP wordpress):
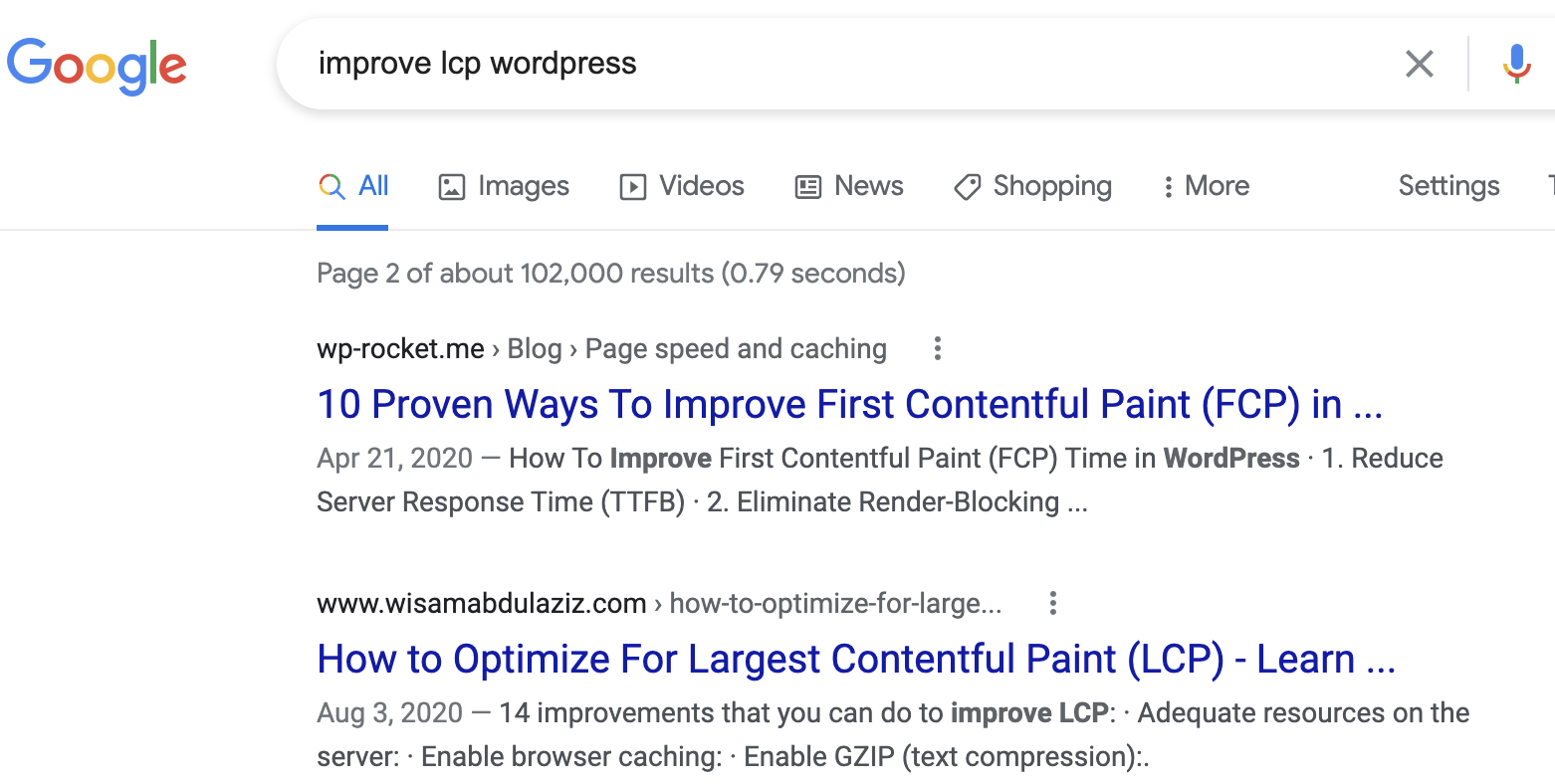
As you can see the title and the description in the SERP for "improve lcp wordpress" are not relevant nor enticing for users to click, my post about LCP is not centered around WordPress, so it is not possible to optimize the title and the description to target this term, re-writing the post or creating a new post could be required in this case.
There is no quick solution that fits all cases, we just need to go through a list of keywords with low CTR, look them up and based on the results come up with recommendations. The most popular fixes to poor CTR are:
- On-page and off-page SEO to improve ranking (better ranking means better CTR)
- Optimize the title tags and descriptions tags to be more relevant to terms with high impressions (no guarantee that Google will use the exact title and description tags)
- Optimize for for featured snippets when applicable, it is very popular to get a low CTR for keywords that trigger featured snippet in SERP as most of the clicks will go to the 0 ranking listing, and many people do not even click on anything if the answer to their question is included in the featured snippet.
Landing page user journey optimization:
Organic search users bounce from a website when:
- They find the information they are looking for very quickly
- They could not find the information they are looking for very quickly (e.g. the landing page was not relevant to what they searched for)
- Bad user experience (could be the design, load time or technical difficulties viewing the page on their device).
How to analyze the landing page user journey:
Optimizing for a landing page user journey starts in Google Analytics by identifying pages with poor performance metrics like:
- High bounce rate
- Low conversion rate
- Low revenue
- Low page/session
- Low session duration
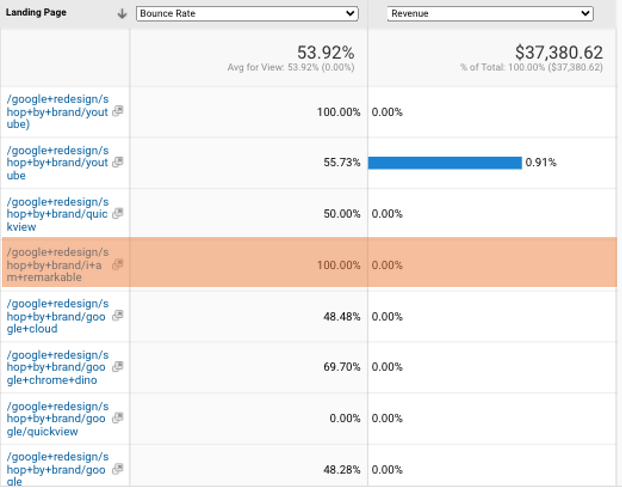
In a quick view for the landing pages performance, a poor page was detected, with a quick look at this page, the reason for that poor performance becomes very clear:
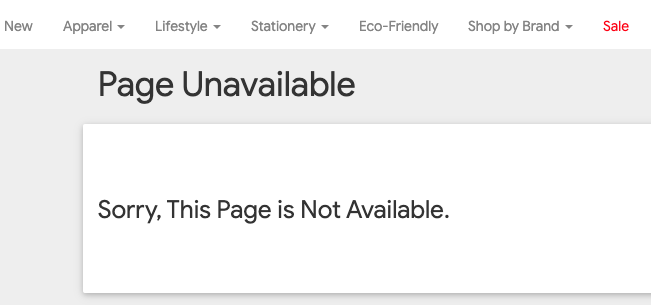
It is a 404 page, the fix in this case could be redirecting this page to another page with similar products, or adding a better call to action that guides users to another relevant page. Let us take another page like this one https://shop.googlemerchandisestore.com/Google+Redesign/Apparel/Google+Dino+Game+Tee which also happens to have a high bounce rate with no conversions. This page sells dino game T-shirts but not a dino game, checking what keywords this page is ranking for will give us an answer to that low performance:

There is no easy solution here as Google Store doesn't sell games, may be a link could be added to their dinosaur game page.
The right approach to analyzing the landing page user journey will enable identifying problems and finding solutions for them.
Conversion funnel user journey optimization:
Conversion journey starts when a user:
- Adds a product to their shopping cart
- Visits a page that contains a lead generation form
- Clicks on any link or button that leads to the two actions above
Tracking this journey for ecommerce websites will be possible if enhanced ecommerce tracking is installed for Google Analytics.
Checking points to optimize for the checkout user journey:
Call to action and message analysis:
The landing page must be optimized for users to take the next step that we want them to take, there are two key elements for that:
- The message on the page
- Call to actions
Adding a call to action like buy now on the product page (see below) could be a quick win:
Shopping behaviour analysis:
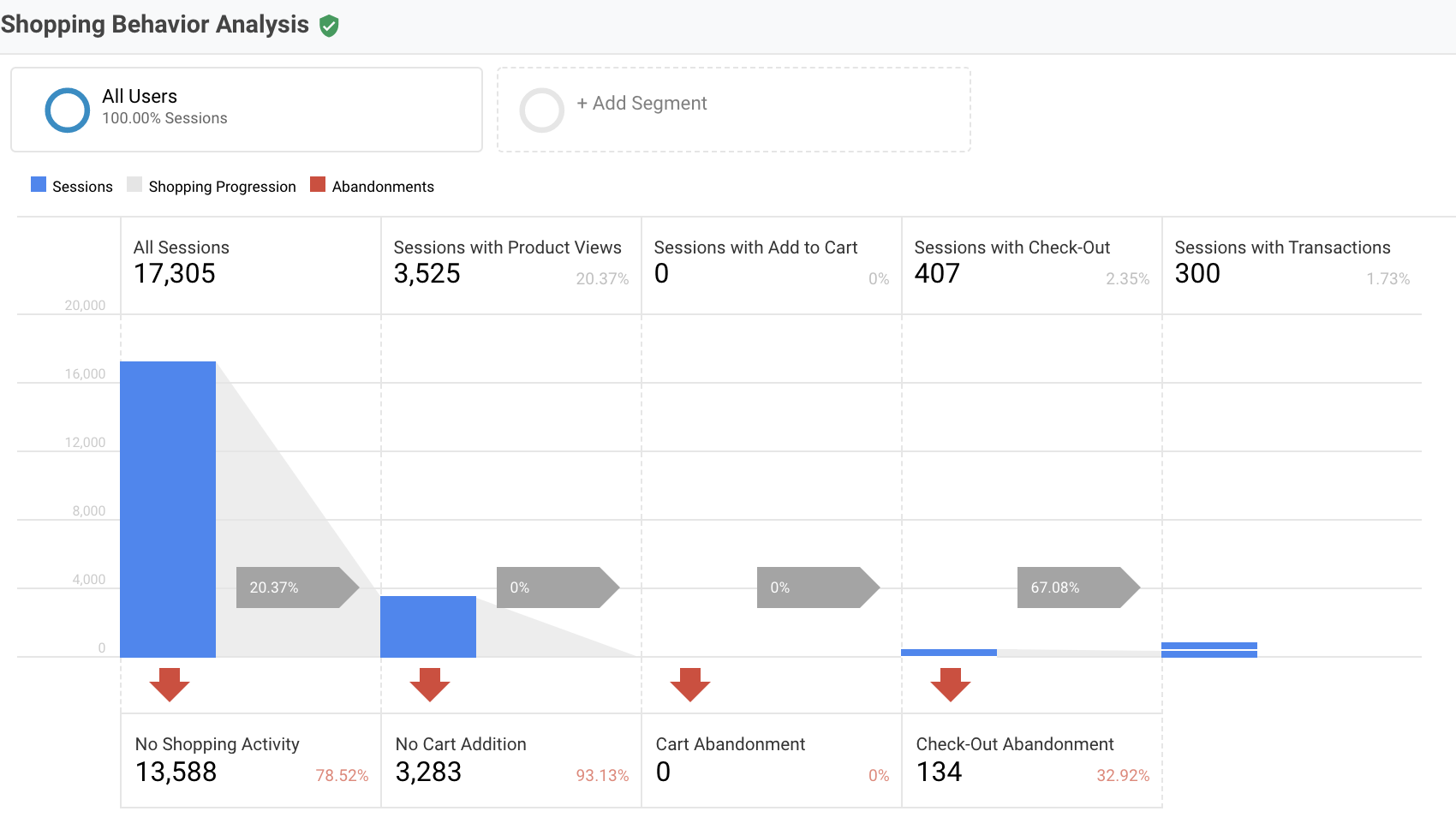
There is a high drop-off rate between all sessions and sessions with product views, and a high drop-off from sessions with product views and sessions with check-out, the changes that can help to reduce drop rate are:
- Better CTAs on product pages (especially for mobile users)
- Relevant products section
- Improving information architecture especially the upper navigation
- Improving the internal search engine
Checkout behaviour analysis:
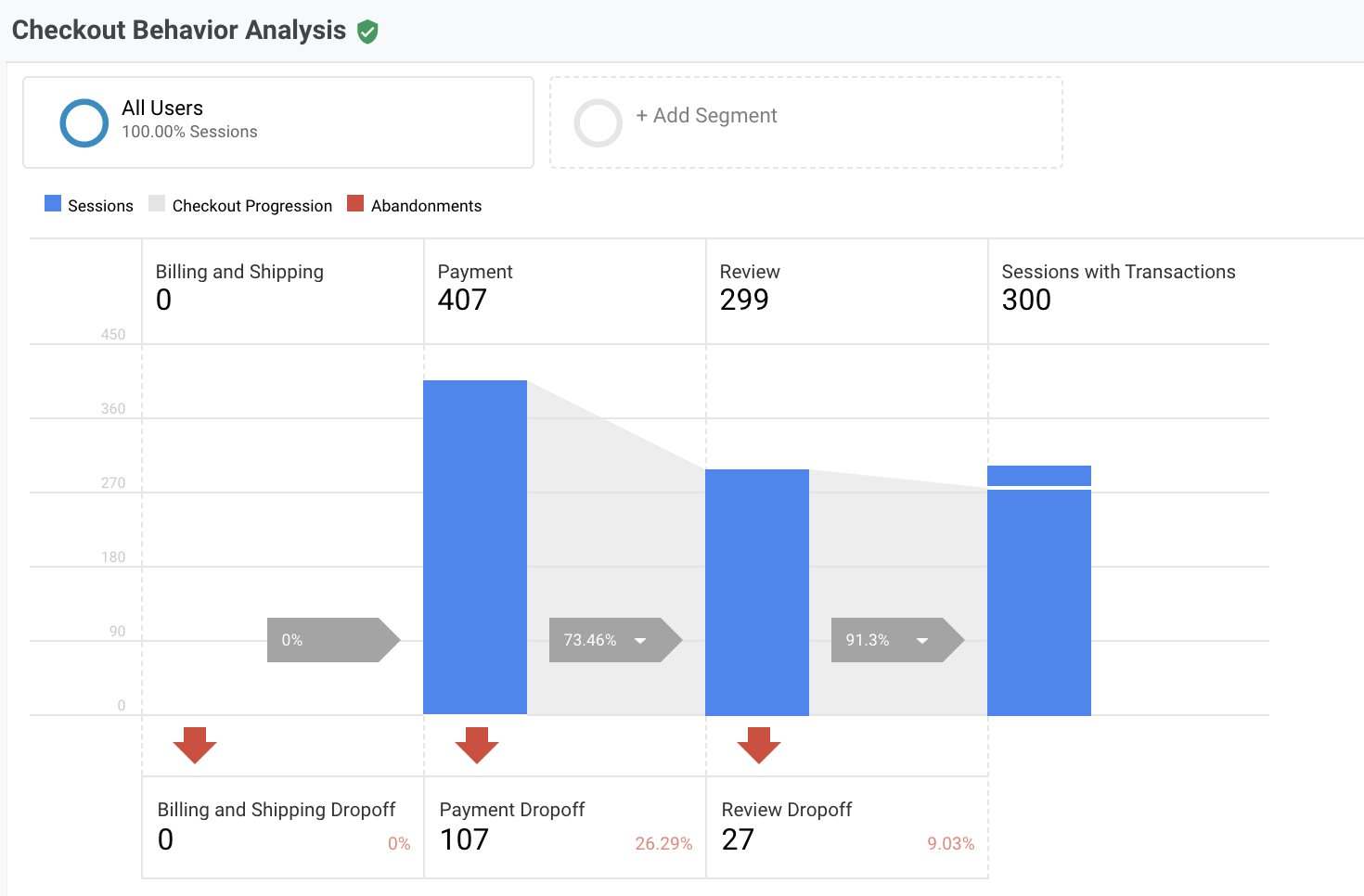
The drop rate from checkout to sessions is not very high, optimizing for the checkout journey could be done in different ways:
- Provide users with as many payment options as possible
- Make prices and shipping cost clear every step of the way
- Reduce the form requirements as much as possible
- Allow checkout without creating an account
- Make sure the checkout process works well on mobile phones and cross browsers
final note:
User journey optimization is not a one time set and forget process, continuous efforts must be spent on a regular basis monitoring and improving all three user journeys.

No Comments