I was hesitant to write a new post about this topic as it is already covered well, in this post I will try to focus more on the diagnoses and recommendations than explaining the reasons behind direct traffic.
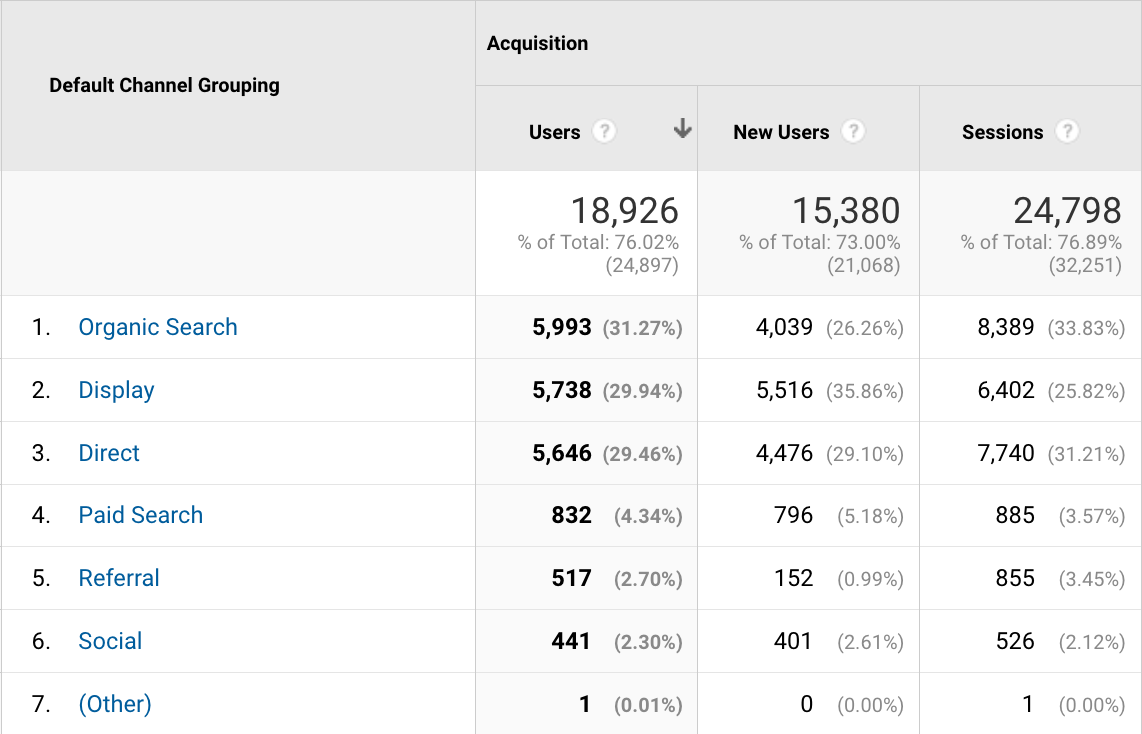
What is direct traffic in Google Analytics:
The popular conception about direct traffic that it is a type-in traffic where people type in the website directly in the browser or visit it using a browser bookmark list, but realty is that it is not always the case, all web tracking software need the referring URL to identify the traffic source, and it comes empty too them they recognize it as a direct traffic.
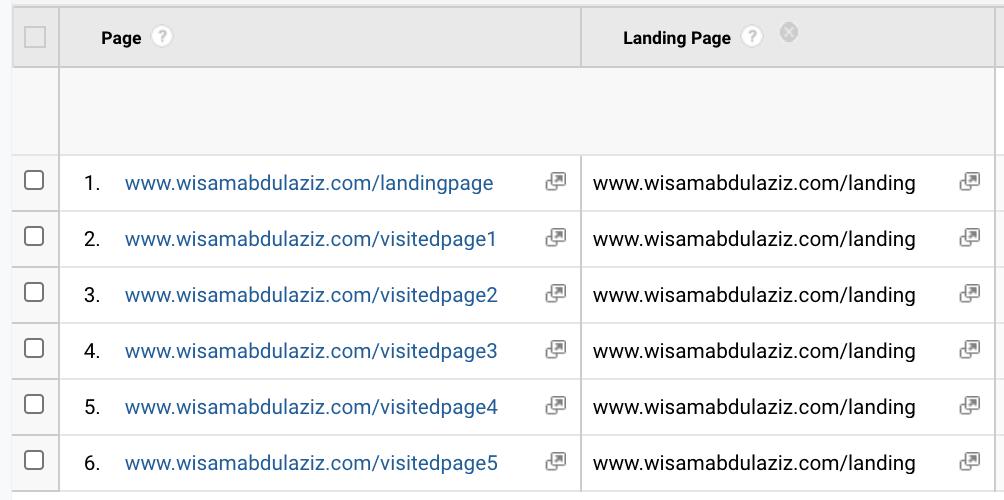
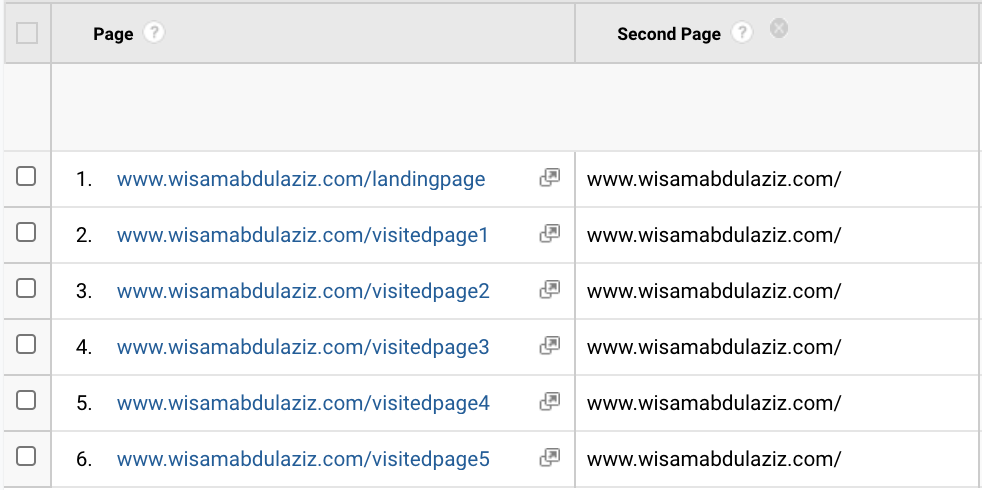
Take this URL as an example https://www.google.com/search?q=seo when Google Analytics detects a URL like that, it compares to its existing list of known sources, they will see that Google.com is listed as a search engine, the q=seo will confirm that it is a search URL not one of Google's properties, the other checking point is to check if the landing page has GCLID in the URL which refers to paid search, GA also checks for any UTM variables that forces GA to override the source. If there is no GCLID or UTMs then GA will categories this medium as organic and the source will be Google.
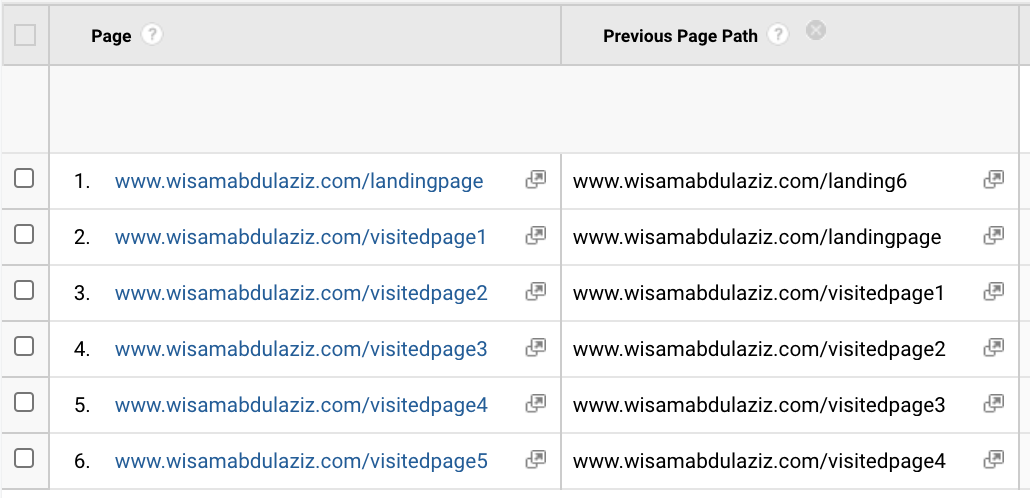
As you can see the referring URL is vital for GA to track any traffic, when the referring URL is missing r the source of the visit will be categorized as direct.
What causes the referring URL to be missing (in other words what causes direct traffic in GA):
The most popular reasons for direct traffic in GA are:
- Excluded referrals in Google Analytics without a proper cross domain tracking
- Type-in traffic (When someone types a website’s URL into their browser, it’s direct traffic) and browser's bookmarks
- Traffic via desktop e-mail clients like Outlook
- Traffic from APPs and desktop software
- Fake direct traffic from spam bots
- Referral traffic from a secure (HTTPS) site to a non-secure (HTTP) site
- Non-web documents like PDF or DOC
- Traffic from incorrectly tagged campaigns (mainly wrong UTM tracking)
- Traffic from links that do not send referral traffic (links with rel="noreferrer" tag)
- Traffic from browsers that block referrals using add-ons or due to firewall settings
I do not want to spend a lot of time explaining what causes direct traffic in GA, especially that many of the reasons above are beyond webmasters control, direct traffic will be always available in GA, it is normal to see 10%-20% direct traffic, no point of fighting, all what webmasters need to do is inspecting the problem and making sure that they have done everything from their end too prevent it.
Diagnosing direct traffic in GA:
Most traffic sources in GA have another tracking point, first thing is to check if GA traffic is matching the numbers provided by other platforms:
- Install Google Search Console and make sure that the organic traffic in a specif time frame matches the number of sessions in Google Analytics for the same time frame
- If you are running Google Ads make sure the number of clicks in Google Ads' dashboard matches the sessions in GA
- Same thing applies to Facebook ads or any other platforms
If the numbers are close that will be a good signal that the most important traffic sources are tracked properly, in the next step I will explain:
How to reduce direct traffic in Google Analytics:
You do not need to worry about every reason for direct traffic, especially the ones you can not control, like type-in traffic, no-referrer etc, direct traffic will be always there, just work on things that are under your control:
- Make sure GA settings are correct and the code is installed on every single page of the website
- Check the referral exclusion section in GA and make sure all excluded domains have cross domain tracking installed.
- Make sure all pages are served with HTTPS with no errors, broken HTTPS can stop browsers from passing referral path and showing traffic as direct
- Tag email campaigns and other marketing channels (especially APPs advertisement) using UTM
- Filter out bot traffic in GA if there is any
Finally just remember, it is almost impossible to reduce direct traffic to zero, 10%-20% is normal, just do your part and keep monitoring and diagnosing any spikes in direct traffic.